Decision making in the emergency room and intensive care unit
Our clinical research is focused on different aspects of emergency and intensive care medicine.
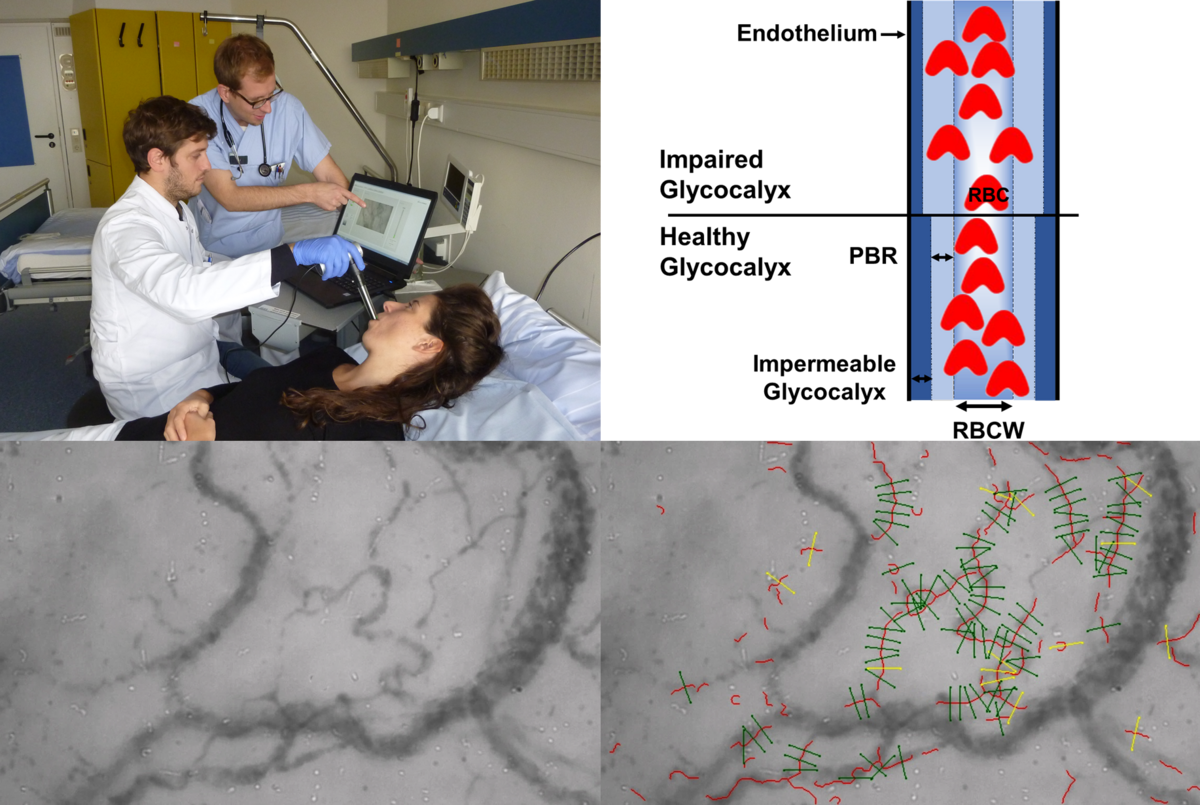
Visualization of sublingual Microcirculation in vivo
Lately, we performed sublingual microcirculatory measurements in patients using sidestream dark field (SDF) in imaging coupled to a novel data acquisition and analysis software (GlycoCheck™) to analyze the perfused boundary region (PBR), an inverse parameter of endothelial glycocalyx dimensions in vessels with diameters of between 5 and 25 µm. We found that the GlycoCheck™ System is a reliable and feasible method to analyze glycocalyx properties performed at bedside in the emergency room (ER) and intensive care unit (ICU). It is conceivable that PBR screening (e.g., at ER admission) might reveal a subgroup of septic patients without apparent end organ-failure (and not yet meeting the Sepsis-3 definition of sepsis) but with overt glycocalyx damage. Given the high chance of further deterioration, such patients might benefit from early, intensive monitoring. Therefore, a prospective, observational study to define PBR cut-offs for risk prediction is currently running in our hospital (Early Detection of Glycocalyx Damage in Emergency Room Patients (EDGE Study, Clinicaltrial.gov Identifier: NCT03126032)).
Decision making in the emergency room and intensive care unit
Another aspect of our clinical research is to identify algorithms and validate biomarkers that could possibly assist decision making in the acute care arena. For example, we have validated an age-adjusted D-dimer cut-off and to assess its utility in elderly patients. The age-adjusted D-dimer cut-off point increases the proportion of older patients, in whom an acute thromboembolic event can be excluded. In another recent project, we questioned the necessity of cerebral imaging in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia. We could show that emergency patients with profound hyponatremia frequently show nonspecific-neurological symptoms and may undergo neuroimaging unnecessarily. The lack of focal neurologic symptoms may serve as a valuable criterion for withholding neuroimaging until hyponatremia has been corrected.
Acute kidney injury and renal replacement therapy
Previous biomarker studies in covered a wide spectrum of markers (NGAL, SDMA, Angiopoietins and NT-proBNP) in different clinical syndromes of acute kidney injury (AKI). For example, we identified serum NGAL (Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin) measured at inception of RRT as an independent predictor of 28-day mortality in ICU patients with dialysis-dependent AKI. In another study, NGAL ≥ 330 ng/ml and presence of AKI (AKIN ≥ I) on admission correctly identified 20 of 24 patients requiring RRT and may serve as an adjunctive tool to improve risk prediction in patients with Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli infection (STEC)-associated haemolytic-uraemic syndrome (HUS). Recently, we analyze renal recovery in a retrospective single-center cohort of patients with dialysis-dependent acute kidney injury (AKI) due to multiple myeloma (MM). Our data suggest a benefit of high-cut-off hemodialysis (HCO-HD) in addition to novel agent-based chemotherapy in serum free light chain removal and renal outcome. In future studies we want to address the concept of active de-resuscitation in RRT-dependent critically-ill patients with significant volume overload.
Related articles:
Hyponatremia upon presentation to the emergency department - the need for urgent neuroimaging studies. Bokemeyer A, Dziewas R, Wiendl H, Schwindt W, Bicsán P, Kümpers P, Pavenstädt H. Sci Rep. 2017 May 16;7(1):1953. PMID: 28512320
Sepsis recognition in the emergency department - impact on quality of care and outcome? Morr M, Lukasz A, Rübig E, Pavenstädt H, Kümpers P. BMC Emerg Med. 2017 Mar 23;17(1):11. PMID: 28330460
Circulating biomarkers for discrimination between aseptic joint failure, low-grade infection, and high-grade septic failure. Ettinger M, Calliess T, Kielstein JT, Sibai J, Brückner T, Lichtinghagen R, Windhagen H, Lukasz A. Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Aug 1;61(3):332-41. PMID: 25870326
Age-adjusted D-dimer cut-offs to diagnose thromboembolic events: validation in an emergency department. Verma N, Willeke P, Bicsán P, Lebiedz P, Pavenstädt H, Kümpers P. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2014 Mar;109(2):121-8. PMID: 23846173
Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in patients with Shiga toxin mediated haemolytic uraemic syndrome (STEC-HUS). Lukasz A, Beneke J, Menne J, Vetter F, Schmidt BM, Schiffer M, Haller H, Kümpers P, Kielstein JT. Thromb Haemost. 2014 Feb;111(2):365-72. PMID: 24172823
Association of angiopoietin-2 and dimethylarginines with complicated course in patients with leptospirosis. Lukasz A, Hoffmeister B, Graf B, Wölk B, Noeckler K, Bode-Böger SM, Hadem J, Pischke S, Kielstein JT. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 30;9(1):e87490. PMID: 24498116
Circulating angiopoietins in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Kümpers P, Nickel N, Lukasz A, Golpon H, Westerkamp V, Olsson KM, Jonigk D, Maegel L, Bockmeyer CL, David S, Hoeper MM. Eur Heart J. 2010 Sep;31(18):2291-300. PMID: 20601390
Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin at inception of renal replacement therapy predicts survival in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Kümpers P, Hafer C, Lukasz A, Lichtinghagen R, Brand K, Fliser D, Faulhaber-Walter R, Kielstein JT. Crit Care. 2010;14(1):R9. PMID: 20122150
Diagnostic value of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) for left ventricular dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5 on haemodialysis. David S, Kümpers P, Seidler V, Biertz F, Haller H, Fliser D. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008 Apr;23(4):1370-7. PMID: 18089624
Angiopoietin-2 predicts disease-free survival after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with high-risk myeloid malignancies. Kümpers P, Koenecke C, Hecker H, Hellpap J, Horn R, Verhagen W, Buchholz S, Hertenstein B, Krauter J, Eder M, David S, Göhring G, Haller H, Ganser A. Blood. 2008 Sep 1;112(5):2139-48. PMID: 18483397
Impact of High-Cut-Off Dialysis on Renal Recovery in Dialysis-Dependent Multiple Myeloma Patients: Results from a Case-Control Study. Gerth HU, Pohlen M, Görlich D, Thölking G, Kropff M, Berdel WE, Pavenstädt H, Brand M, Kümpers P. PLoS One. 2016 May 6;11(5):e0154993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154993. eCollection 2016. PMID: 27152520

